前言
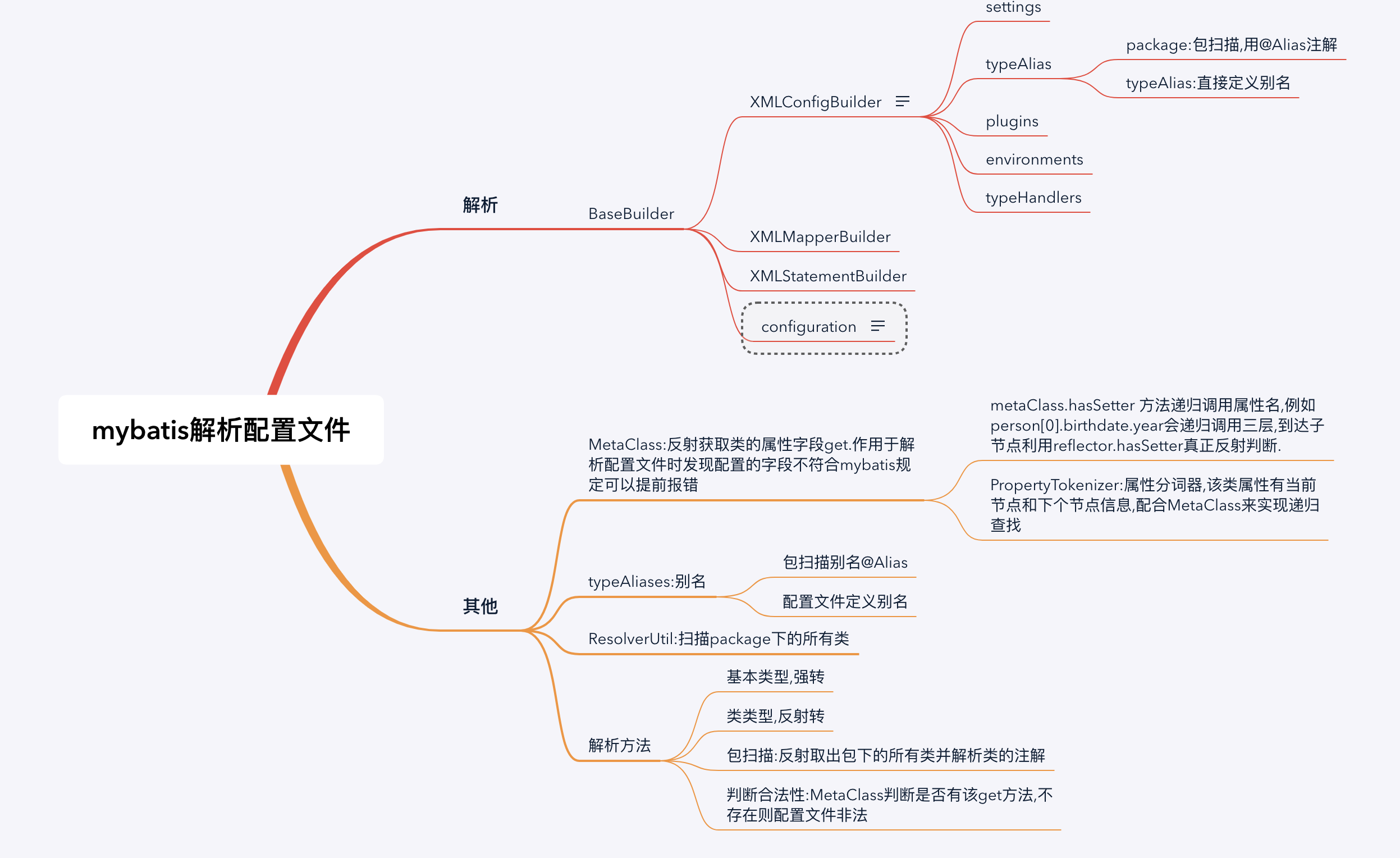
mybatis的配置文件解析这块时mybatis工作的前提,理解mybatis的工作原理必定要先理解mybatis是如何把你配置xml(数据库database,settings,typeAlias,plugins)装载到内存中启动.
在分析解析源码前先理解这几个类的职责:
configuration:所有的配置文件信息都会装载在这个类中,意思是这个类拥有你写在配置文件的所有信息.
XMLConfigBuilder:xml配置文件的建造者,解析配置文件的入口.
BaseBuilder:建造者基类,所有的建造者都继承该类.
ResolverUtil:用于便利包下面的类的工具类.
MetaClass:反射获取类的属性字段get方法.作用于解析配置文件时发现配置的字段不符合mybatis规定可以提前报错.
BaseBuilder继承关系图:
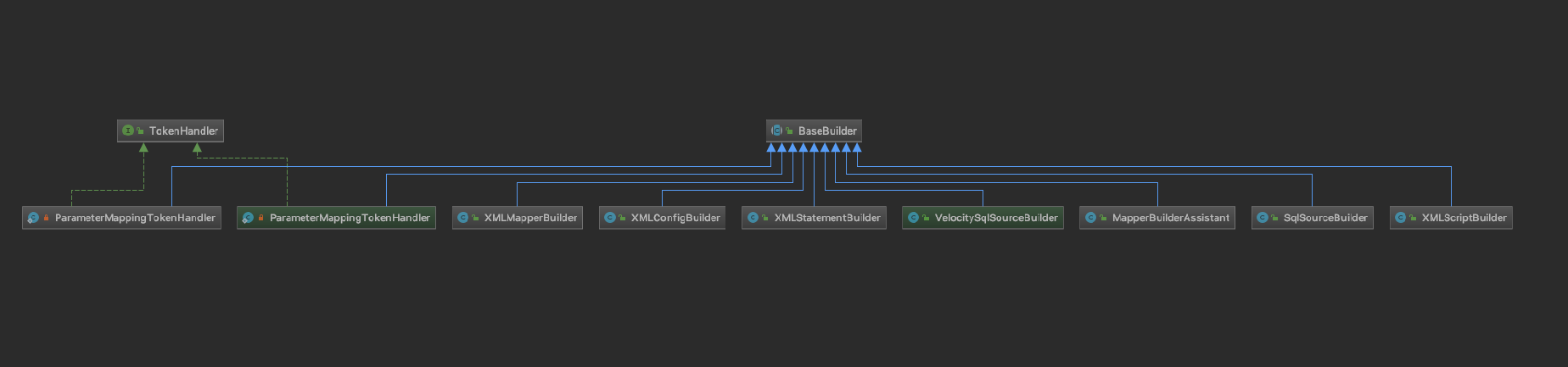 而我们这次只需要关注XMLConfigBuilder建造者类.
而我们这次只需要关注XMLConfigBuilder建造者类.
XMLConfigBuilder
该类是简析配置文件的入口,主要用了xpath对xml进行解析
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
//第4种方法是最常用的,它使用了一个参照了XML文档或更特定的SqlMapConfig.xml文件的Reader实例。
//可选的参数是environment和properties。Environment决定加载哪种环境(开发环境/生产环境),包括数据源和事务管理器。
//如果使用properties,那么就会加载那些properties(属性配置文件),那些属性可以用${propName}语法形式多次用在配置文件中。和Spring很像,一个思想?
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//委托XMLConfigBuilder来解析xml文件,并构建
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
//这里是捕获异常,包装成自己的异常并抛出的idiom?,最后还要reset ErrorContext
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
}
//解析配置
public Configuration parse() {
//如果已经解析过了,报错
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//根节点是configuration
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
//解析配置
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//分步骤解析
//issue #117 read properties first
//1.properties
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//2.类型别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//3.插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//4.对象工厂
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
//5.对象包装工厂
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
//6.设置
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//7.环境
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//8.databaseIdProvider
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//9.类型处理器
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//10.映射器
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
由上面可以看出对configuration和configuration下面的子节点完全是硬编码解析. 下面挑选settings和typeAliases分析里面解析代码,其他节点大致相同.
settings节点
看下settings节点的例子
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="enhancementEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25000"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>
private void settingsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
//检查下是否在Configuration类里都有相应的setter方法(没有拼写错误)
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
//下面非常简单,一个个设置属性
//如何自动映射列到字段/ 属性
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
//缓存
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
//proxyFactory (CGLIB | JAVASSIST)
//延迟加载的核心技术就是用代理模式,CGLIB/JAVASSIST两者选一
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
//延迟加载
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
//延迟加载时,每种属性是否还要按需加载
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), true));
//允不允许多种结果集从一个单独 的语句中返回
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
//使用列标签代替列名
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
//允许 JDBC 支持生成的键
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
//配置默认的执行器
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
//超时时间
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
//是否将DB字段自动映射到驼峰式Java属性(A_COLUMN-->aColumn)
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
//嵌套语句上使用RowBounds
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
//默认用session级别的缓存
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
//为null值设置jdbctype
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
//Object的哪些方法将触发延迟加载
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
//使用安全的ResultHandler
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
//动态SQL生成语言所使用的脚本语言
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
//当结果集中含有Null值时是否执行映射对象的setter或者Map对象的put方法。此设置对于原始类型如int,boolean等无效。
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
//logger名字的前缀
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
//显式定义用什么log框架,不定义则用默认的自动发现jar包机制
configuration.setLogImpl(resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl")));
//配置工厂
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
}
这里有几个需要注意地方
- 刚开始对settings的节点做校验,用了MetaClass类,该类的作用是反射获取类的属性Get方法.主要是用来娇艳settings节点里面配置的子节点是否都是Configuration里面字段,对于非法的字段直接报错.
PropertyTokenizer:属性分词器,该类属性有当前节点和下个节点信息,配合MetaClass来实现递归查找.
- 对于普通类型的配置只需要强转,但对于一些类类型就需要反射实例化.
typeAliases节点
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
<typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/>
<typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/>
<typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/>
<typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/>
<typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/>
</typeAliases>
//or
<typeAliases>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
</typeAliases>
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
//如果是package
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
//(一)调用TypeAliasRegistry.registerAliases,去包下找所有类,然后注册别名(有@Alias注解则用,没有则取类的simpleName)
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
//如果是typeAlias
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
//根据Class名字来注册类型别名
//(二)调用TypeAliasRegistry.registerAlias
if (alias == null) {
//alias可以省略
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
该方法主要对两种别名配置适配.主要有两个方面需要注意
- typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias别名注册方法,该方法有很多从在重载方法,但最终都是为TypeAliasRegistry类里面的TYPE_ALIASES HashMap塞值,
该TYPE_ALIASES key为别名,value为别名对应的类,默认情况下,mybatis已经初始化了很多别名,例如int,byte,long等等. TypeAliasRegistry和configuration同级,同属于BaseBuilder的属性
- 包扫描下,是通过扫描包下面的所有类,并找出@Alias注解定于的别名,没有写该注解默认类的简单名字为别名.
通过ResolverUtil类反射获取包下的所有类. TypeAliasRegistry是configuration的属性,这点和直接配置的别名是不同的.猜测这是别名优先级的问题,优先以BaseBuilder为准.
设计模式
xmind